Access EVM accounts
This tutorial illustrates how to use crates from the Frontier project to build an Ethereum-compatible blockchain that can access Ethereum-based accounts and execute Solidity-based smart contracts. The two main goals of the Frontier project are to enable you to do the following:
- Run Ethereum decentralized apps unmodified using local Substrate nodes.
- Import state from the Ethereum main network.
This tutorial uses a predefined node template to provide a working environment. The template was generated using the instructions in the Frontier release guide.
If you want to generate a standalone template for yourself, you can use the node-template-release.sh template generation script.
If you build your own node using from the frontier repository or using the template generation script, be aware that Frontier uses its own versions of Substrate crates and you might need to update the dependencies in your Cargo files to match the dependencies in your project.
Before you begin
You should have completed the following Substrate tutorials before attempting this tutorial:
From the tutorials, you should be familiar with how to perform the following tasks:
- Launch a Substrate blockchain node.
- Add, remove, and configure pallets in a runtime.
- Submit transactions by connecting to a node using Polkadot-JS or another front-end.
Before starting this tutorial, you should also be familiar with the following:
- Ethereum core concepts and terminology
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) basics
- Decentralized applications and smart contracts
- Pallet design principles
Genesis configuration
The development chain specification in the frontier-node-template defines a genesis block that is been pre-configured with an EVM account for the alice account.
When you start this node in development mode, the EVM account for alice is funded with a default amount of Ether.
You'll be using this account to view EVM account details and to call Ethereum smart contracts.
After you start the node, you'll be able to use the Polkadot-JS application to see the details of the EVM account for alice.
Compile a Frontier node
The Frontier node template provides a working development environment so that you can start building on Substrate right away.
To compile the Frontier node template:
- Open a terminal shell on your computer.
-
Clone the node template repository by running the following command:
git clone https://github.com/substrate-developer-hub/frontier-node-template.git -
Change to the root of the node template directory by running the following command:
cd frontier-node-template -
Compile the node template by running the following command:
cargo build --release
Connect to the node
After your node compiles, you must start the node to begin exploring the preconfigured EVM accounts.
To start the local Substrate node:
- Open a terminal shell on your local computer, if needed.
- Change to the root directory where you compiled the
frontier-node-template. -
Start the node in development mode by running the following command:
./target/release/frontier-template-node --devThe
--devcommand-line option specifies that the node runs using the predefineddevelopmentchain specification that includes the predefined EVM account foraliceand other accounts for testing. -
Verify your node is up and running successfully by reviewing the output displayed in the terminal.
The terminal should display output similar to this:
2022-07-08 10:06:42 Frontier Node 2022-07-08 10:06:42 ✌️ version 0.0.0-1b6bff4-x86_64-macos 2022-07-08 10:06:42 ❤️ by Substrate DevHub <https://github.com/substrate-developer-hub>, 2021-2022 2022-07-08 10:06:42 📋 Chain specification: Development 2022-07-08 10:06:42 🏷 Node name: flippant-boat-0444 2022-07-08 10:06:42 👤 Role: AUTHORITY ... - Connect to the local node using the Polkadot-JS application.
-
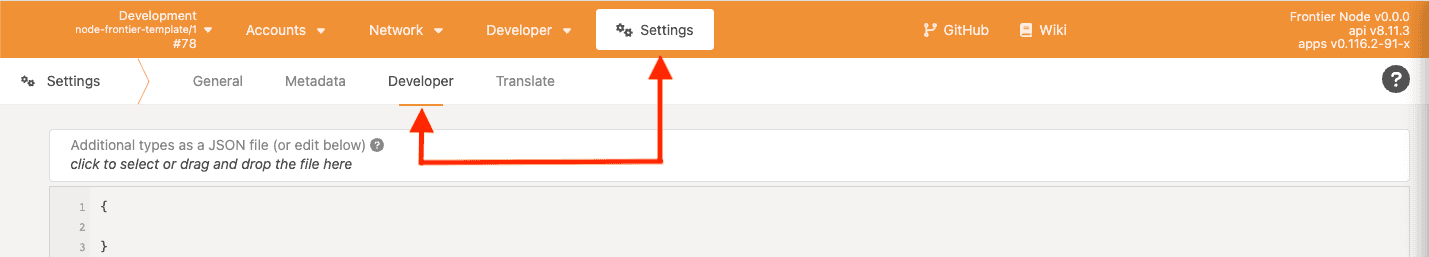
Click Settings, then click Developer.
![Developer settings]()
-
Define the following account information to create an EVM
Accounttype and enable the account to send transactions and to inspect blocks.To send transactions, you must define
AddressandLookupSourcesettings.
To inspect blocks, you must defineTransactionandSignaturesettings.{ "Address": "MultiAddress", "LookupSource": "MultiAddress", "Account": { "nonce": "U256", "balance": "U256" }, "Transaction": { "nonce": "U256", "action": "String", "gas_price": "u64", "gas_limit": "u64", "value": "U256", "input": "Vec<u8>", "signature": "Signature" }, "Signature": { "v": "u64", "r": "H256", "s": "H256" } } - Click Save.
Query balances using RPC
After you have configured settings for the EVM account, you can use the Polkadot-JS application to view information about the EVM account for alice.
- Verify that your node is still running and the Polkadot-JS application is connected to the node.
- Click Developer, then select RPC calls.
- On the Submission tab, select eth as the endpoint to call.
- Select getBalance(address, number) from the list of functions to call.
-
Specify the EVM account identifier for the
aliceaccount for the address.The predefined account address is
0xd43593c715fdd31c61141abd04a99fd6822c8558. The address for the account was calculated from the public key for thealiceaccount using Substrate EVM utilities. -
Click Submit RPC call.
The call should return output similar to the following:
2: eth.getBalance: U256 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,210,955
Deploy a smart contract
Now that you'e seen how to query the balance for an Ethereum address, you might want to explore how you can deploy and call Ethereum smart contracts and test the related functionality. This tutorial uses a Truffle sample contract that defines an ERC-20 token. You can also create an ERC-20 token contract using Polkadot JS SDK and Typescript.
-
Create the ERC-20 contract.
For convenience, you can use the compiled
bytecodefrom the token contract in MyToken.json to deploy the contract on the Substrate blockchain. - Verify that your node is still running and the Polkadot-JS application is connected to the node.
- Click Developer, then select Extrinsics.
- Select the ALICE development account as the account used to submit the transaction.
- Select evm.
- Select the create function.
-
Configure the parameters for the function.
For this Specify this source0xd43593c715fdd31c61141abd04a99fd6822c8558 initraw bytecodehex value fromMyToken.jsonvalue0 gasLimit4294967295 maxFeePerGas100000000 You can leave optional parameters empty. The value for the
noncewill increment the known nonce for the source account, starting from0x0. Depending on the function you selected, you might need to remove unused parameters. - Click Submit Transaction.
- Click Sign and Submit to authorize the transaction.
View the smart contract
After you submit the transaction, the contract is deployed on the network and you can view information about it using the Polkadot-JS application.
- Verify that your node is still running and the Polkadot-JS application is connected to the node.
- Click Network, then select Explorer.
-
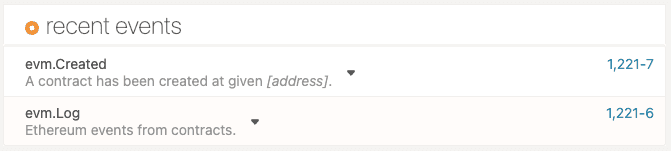
Click the evm.Created event to verify the address of the newly-created contract is
0x8a50db1e0f9452cfd91be8dc004ceb11cb08832f.![Successful contract created event]()
You can also view details about the transaction using the Console in the Developer Tools for your browser.
Because EVM contract addresses are determined by the account identifier and nonce of the contract creator, the address where the contract is deployed is calculated using the well-known account identifier
0xd43593c715fdd31c61141abd04a99fd6822c8558and nonce0x0for thealiceaccount. - Click Developer, then select Chain State.
- Select evm as the state to query and accountCodes.
- Specify the account identifier
0xd43593c715fdd31c61141abd04a99fd6822c8558for thealiceaccount and notice that the account code is empty (0x) - Specify the contract address
0x8a50db1e0f9452cfd91be8dc004ceb11cb08832ffor the contract you deployed using thealicedevelopment account and notice that contract account code is the bytecode from the Solidity contract.
View account storage
The ERC-20 contract you deployed is based on the OpenZeppelin ERC-20 implementation. This contract includes a constructor that mints a maximum number of tokens and stores them in the account associated with the contract creator.
To query the account storage associated with the smart contract:
- In Chain State with evm as the state to query, select accountStorages.
- Specify the ERC-20 contract address
0x8a50db1e0f9452cfd91be8dc004ceb11cb08832fas the first parameter. -
Specify the storage slot to read as the second parameter
0x045c0350b9cf0df39c4b40400c965118df2dca5ce0fbcf0de4aafc099aea4a14.The storage slot for the address was calculated using Substrate EVM utilities based on slot 0 and the account identifier
0xd43593c715fdd31c61141abd04a99fd6822c8558.The value that is returned should be
0xffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff.If you check the balance for the
aliceaccount after deploying the contract, you see that a fee was withdrawn from the account and thegetBalance(address, number)call returns a value similar to the following:340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,603,530,233,757,803
Transfer tokens
So far, you have worked exclusively with the alice development account.
The next step is to use the deployed contract to transfer tokens to another account.
- Verify that your node is still running and the Polkadot-JS application is connected to the node.
- Click Developer, then select Extrinsics.
- Select the ALICE development account as the account used to submit the transaction.
- Select evm.
- Select call to invoke the
transfer(address, uint256)function on the ERC-20 contract. -
Configure the parameters for the function.
For this Specify this source0xd43593c715fdd31c61141abd04a99fd6822c8558 target0x8a50db1e0f9452cfd91be8dc004ceb11cb08832f input0xa9059cbb0000000000000000000000008eaf04151687736326c9fea17e25fc528761369300000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000dd value0 gasLimit4294967295 maxFeePerGas100000000 The
sourcerepresents the account holding the tokens. In this case, thesourceis the EVM account foralice, the contract creator. Thetargetis the contract address for the transfer of tokens fromalicetobob.The
inputparameter is an EVM ABI-encoded function call that specifies the function call to perform a transfer (0xa9059cbb) and the arguments the function requires. For this function, the arguments are thebobEVM account identifier (0x8eaf04151687736326c9fea17e25fc5287613693) and the number of tokens to be transferred (221 or0xddin hex).The input value in this tutorial was calculated using the Remix web IDE.
- Click Submit Transaction.
- Click Sign and Submit to authorize the transaction.
Verify the token transfer
After you submit the transaction, you can verify the token transfer using the Polkadot-JS application.
- Verify that your node is still running and the Polkadot-JS application is connected to the node.
- Click Network, then select Explorer.
-
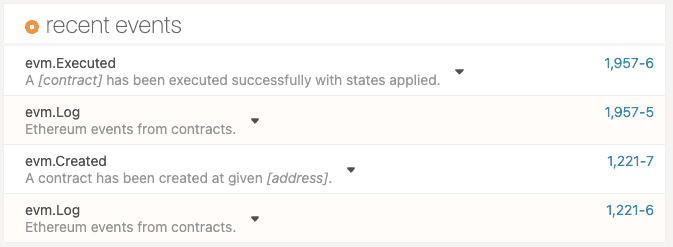
Click the evm.Executed event to verify the address of the executed contract is
0x8a50db1e0f9452cfd91be8dc004ceb11cb08832f.![Successful execution event]()
- Click Developer, then select Chain State.
- Select evm as the state to query and accountStorages.
-
Check the storage for the contract address
0x8a50db1e0f9452cfd91be8dc004ceb11cb08832fand storage slot0x045c0350b9cf0df39c4b40400c965118df2dca5ce0fbcf0de4aafc099aea4a14.0xffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff22If you check the balance for the
aliceaccount after deploying the contract, you see that a fee was withdrawn from the account and thegetBalance(address, number)call returns a value similar to the following:340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,603,530,233,366,411